Notifications
SUN PROTECTION
In India, cosmetic is defined as any article intended to be rubbed, poured, sprinkled, or sprayed on, or introduced into, or otherwise applied to the human body or any part thereof for cleansing, beautifying, promoting attractiveness or altering the appearance, and includes any article intended for use as a component of cosmetic.1 Now-a-days one cosmetic product category sunscreen have gain wide popularity due to additional health benefits apart from beautification.2-3 Either separate sunscreens or many other sunscreen loaded cosmetic products for skin care, hair care, lips care and eye care are available in market.4-7 This review is tried to summarize all possible issues related to sunscreens.
Ultra-Violet radiations and human skin8-9
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is defined as that portion of the electromagnetic radiation lies between X-rays and visible light which is from 200 to 400 nm.
This ultraviolet radiation comprises 3 categories depending on wavelength as follows:
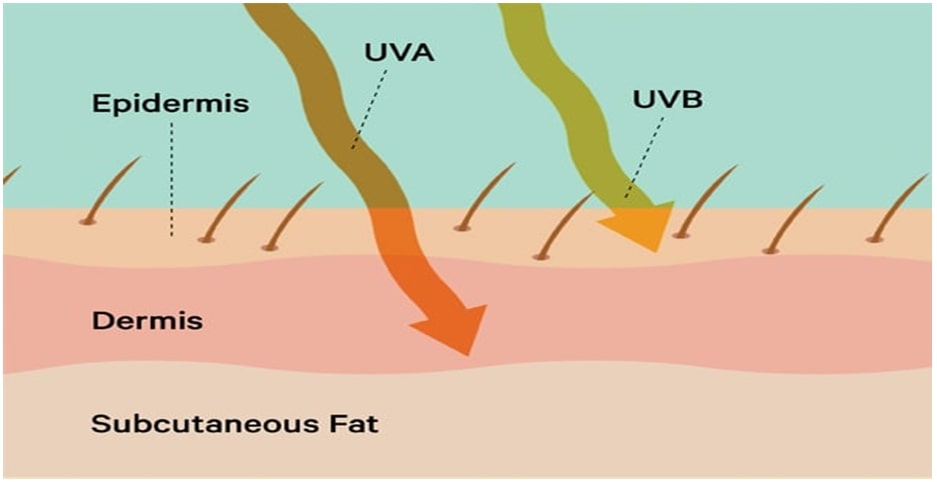
• UV-A Radiation: This radiation ranges between 320 to 400 nm. UV-A is most responsible radiation for immediate tanning or darkening of the skin due to excess production of melanin in the epidermis, premature photo ageing, suppression of immunologic functions, and even necrosis of endothelial cells and damage of dermal blood vessels
• UV-B Radiation: This radiation ranges between 280 to 320 nm. UV-B radiations are known as burning rays as they are 1000 times more capable of causing sunburn than UV-A. UV-B rays act mainly on the epidermal basal cell layer of the skin but more genotoxic than UV-A radiations. Ultraviolet B (UVB) rays vary with time and season are major cause of sunburn. Sunburned skin is a leading risk factor for melanoma and non-melanoma skin cancer.
• UV-C Radiation: This radiation ranges between 200 to 280 nm. UV-C radiations are filtered by stratospheric ozone layers so less effective and hazardous. The human skin is the largest organ of the body of surface area of approximately 1.5–2.0 m2. Skin acts as effective barrier against the harmful effects of environmental and xenobiotic agents.9-10 Among all factor chronic exposure of UV radiations is key factor in instigation of skin problems like cracks, burns, immune suppression, wrinkles, dermatitis, urticaria, ageing, hypopigmentation, hyperpigmentation and most complicated skin cancers.11 Role of infrared radiations in skin damage is unclear.
How to protect your skin from the sun
Use sunscreen every day, even if it’s cloudy.
Apply at least one ounce of sunscreen (enough to fill a shot glass) at least 15 to 30 minutes before going outside. Also use a lip balm or lipstick that contains sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 30.
Choose a broad spectrum sunscreen that protects against both UVA and UVB radiation. Make sure it is water resistant and has a SPF of 30 or higher. Other sunscreens may help keep you from getting sunburned, but they won’t protect against skin cancer.
Reapply sunscreen every two hours. Reapply every hour if you are swimming or sweating. Be extra careful around water and sand. These surfaces reflect the damaging rays of the sun, which can increase your chance of getting a sunburn.
Keep babies younger than 6 months old completely covered and in the shade.
Limit the amount of time you’re in the sun between 10:00 AM and 4:00 PM. This is when the sun's rays are the most intense. Practice the shadow rule: if your shadow is shorter than you, the sun's rays are at their strongest, and you should find shade.
If possible, wear a long-sleeved shirt and long pants. Dark clothing with tightly woven fabric blocks more sun than white or loosely woven fabrics. For additional protection, look for clothes made with special sun-protective materials.
Accessorize with a hat that shades your face, neck, and ears and a pair of sunglasses. Sunglasses with lenses that have 99% to 100% UV absorption provide optimal protection for the eyes and the surrounding skin. Be even more cautious if you are taking medications that may make you more sensitive to the sun. These include specific types of antibiotics, anti-inflammatories, antifungals, blood pressure medications, and chemotherapies